What is Net Promoter Score (NPS)?

In today’s customer-centric world, businesses need a clear way to measure customer satisfaction and loyalty. That’s where Net Promoter Score (NPS) comes in. NPS isn’t just another metric—it’s a simple yet powerful tool that helps organizations understand how their customers truly feel about their products or services.
In this post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of NPS, why it matters, how it’s calculated, and practical ways you can use it to grow your business and keep your customers happy.
What is Net Promoter Score (NPS)?
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a customer feedback metric that measures how likely your customers are to recommend your business to others. It’s based on a straightforward question:
“On a scale from 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to a friend or colleague?”
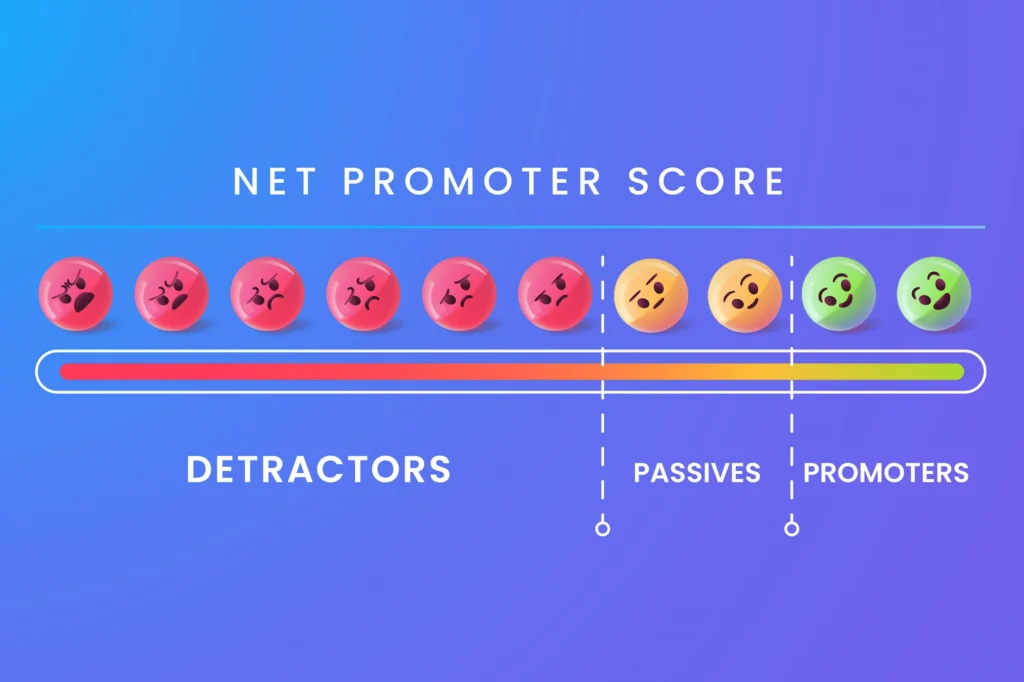
Customers are grouped into three categories based on their responses:
- Promoters (9-10): Loyal enthusiasts who love your brand.
- Passives (7-8): Satisfied but not overly enthusiastic customers.
- Detractors (0-6): Unhappy customers who may harm your reputation through negative word-of-mouth.
Your NPS score is then calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters.
Why is NPS Important for Teams?
Net Promoter Score is not just about customers; it’s also a powerful tool for teams. Here’s why:
1. Customer-Centric Insights: NPS gives teams a direct line to customer feedback. Knowing what’s working and what’s not helps them refine their strategies.
2. Goal Alignment: When everyone knows the NPS, it becomes easier to align efforts across departments to improve the score.
3. Motivational Impact: A high NPS boosts morale, while a low score serves as a rallying call for improvement.
For example, consider a marketing team that learns their campaigns are converting promoters. They can double down on successful strategies while troubleshooting areas with more detractors.
How is NPS Calculated?
The Net Promoter Score formula might be simple, but the insights it provides are profound. Let’s break it down:
1. Survey Your Audience: Ask your customers the classic NPS question.
2. Categorize Responses: Sort them into promoters, passives, and detractors based on their ratings.
3. Crunch the Numbers: Subtract the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters.
Here’s an example:
- You survey 100 customers.
- 50 rate you as promoters, 30 as passives, and 20 as detractors.
- NPS = (50% – 20%) = 30
An NPS of 30 indicates a positive experience but also leaves room for improvement.
What is a Good NPS Score?
What constitutes a “good” NPS score depends on the industry. However, here are some general benchmarks:
- Above 50: Excellent—your customers are highly loyal.
- 30-50: Good—you’re meeting expectations, but there’s room for growth.
- 0-30: Average—your business is doing okay but could improve.
For instance, the tech industry often boasts higher scores, while service industries might find achieving above 30 to be commendable. The key is to aim higher than your industry average.
What is a Bad NPS Score?
A negative NPS score means you have more detractors than promoters. This is a red flag that signals:
- Unmet Expectations: Customers are dissatisfied with your product or service.
- Reputation Risks: Detractors might actively dissuade others from choosing your brand.
- Revenue Decline: Unhappy customers often lead to lost sales and lower lifetime value.
Companies with low NPS scores must act quickly, identifying and addressing the pain points causing dissatisfaction.
Transactional vs. Relational NPS Programs
When implementing NPS, businesses often choose between transactional and relational programs. Each serves a different purpose and fits unique scenarios.
Transactional NPS
This approach focuses on feedback after specific interactions, like completing a purchase or engaging with customer support. For example:
- Purpose: Evaluate the quality of a particular experience.
- Timing: Surveys are sent immediately after the transaction.
- Use Case: Identifying and improving pain points in specific processes.
Relational NPS
Relational surveys, on the other hand, gauge overall customer loyalty at regular intervals.
- Purpose: Understand long-term sentiment toward your brand.
- Timing: Sent quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
- Use Case: Benchmarking performance over time and identifying broader trends.
Both methods are essential. A business might use transactional NPS to fix immediate issues while leveraging relational Net Promoter Score for strategic insights.
What Can You Measure Using NPS?
NPS isn’t just about asking a single question. It’s a versatile tool that can measure various aspects of the customer journey, including:
- Customer Loyalty: The primary metric NPS tracks, providing a snapshot of overall satisfaction.
- Touchpoint Performance: Analyze specific stages, such as onboarding, product delivery, or customer support.
- Brand Perception: Understand how customers feel about your company in comparison to competitors.
- Feedback Trends: Track sentiment changes over time to identify patterns in satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
For instance, a SaaS company might use NPS to evaluate how easy it is for users to get started with their software. By measuring these facets, businesses can uncover actionable insights to drive improvement.
What is eNPS?
While traditional NPS focuses on customers, eNPS (Employee Net Promoter Score) measures employee satisfaction and loyalty. The concept is similar: employees are asked how likely they are to recommend their workplace to others.
Benefits of eNPS
- Employee Engagement: A strong eNPS correlates with higher productivity and morale.
- Workplace Improvement: Identifies internal issues and opportunities for better team management.
Limitations of eNPS
- Limited Context: A single score doesn’t reveal the full picture of employee sentiment.
- Anonymous Feedback Challenges: Employees may fear repercussions, leading to biased responses.
- Actionability: It requires follow-up surveys or discussions to uncover root causes.
While eNPS is a useful starting point, it’s most effective when combined with other employee feedback mechanisms.
How to Run Surveys and Collect NPS Feedback
Collecting accurate and meaningful Net Promoter Score (NPS) feedback requires careful planning. Here’s how to do it right:
1. Choose the Right Tool
Leverage survey platforms like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or specialized NPS tools such as Delighted or AskNicely.
2. Time It Right
Send surveys when customers are most likely to respond thoughtfully:
- After completing a purchase or using your service.
- During a quiet period in their relationship with your brand.
3. Keep It Short
- Stick to the NPS question and one or two follow-up questions.
- Example: “What’s the reason for your score?”
4. Personalize Your Outreach
Use the customer’s name and reference their specific interaction for a tailored feel.
5. Offer Incentives (If Appropriate)
Encourage responses by offering a small incentive, such as a discount or gift card.
A well-executed Net Promoter Score survey ensures higher response rates and more actionable feedback.
How to Interpret Your NPS Score
Once you’ve collected responses and calculated your score, the next step is interpretation.
Analyze Trends
- Look at trends over time rather than focusing solely on a single score.
- Identify patterns—are certain times of the year consistently better or worse?
Segment Responses
- Break down feedback by customer demographics or touchpoints to find areas of strength and weakness.
Turn Qualitative Feedback into Action
- Use open-ended responses to dive deeper into the “why” behind the score.
- For example, if several detractors cite slow shipping, prioritize improving your logistics.
NPS interpretation isn’t just about the number—it’s about what you do with it.
What Can You Do with Your NPS Score?
So you’ve got your NPS score. Now what? Here’s how to put it to good use:
- Enhance Customer Experience: Use feedback to identify and improve weak spots.
- Reward Promoters: Thank loyal customers with special offers, exclusive perks, or shout-outs.
- Win Back Detractors: Reach out to dissatisfied customers and address their concerns directly.
- Inform Marketing Strategies: Use positive feedback as testimonials or case studies.
For example, a company might create a referral program that encourages promoters to bring in new customers, boosting both loyalty and acquisition.
How to Improve a Low NPS
Step 1: Identify Root Causes
Analyze detractor feedback to find common complaints. Group similar issues, such as product quality or customer service, to identify the most critical problems impacting your score.
Step 2: Prioritize Key Areas
Focus on fixing the issues that matter most to your customers. Address the pain points with the highest impact, like long response times or defective products, to see immediate improvements.
Step 3: Communicate Transparently
Inform customers that you’ve heard their concerns and share your plans to address them. A simple acknowledgment can rebuild trust and show you’re committed to improvement.
Step 4: Train Your Team
Equip employees with the skills to deliver excellent service. Conduct training sessions focused on resolving common customer complaints and improving communication.
Step 5: Monitor Progress
Regularly track your Net Promoter Score and feedback to measure the success of your efforts. Continuous monitoring ensures you’re on the right path and allows for further adjustments.
Improving Net Promoter Score takes time, but with these steps, you can turn customer dissatisfaction into long-term loyalty.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is more than just a number; it’s a window into your customers’ hearts. By measuring loyalty, identifying pain points, and taking action, you can create experiences that delight and retain your audience. Whether you’re just starting with NPS or refining an existing program, the insights it offers can propel your business forward.

